Bold, italics and underlining
Introduction
Simple text formatting helps to highlight important concepts within a document and make it more readable. Using italics, bold or underlined words can change the perception of the reader.
In this article three basic text formatting tools will be explained: italics, bold and underline. Let's begin with an example:
Some of the \textbf{greatest}
discoveries in \underline{science}
were made by \textbf{\textit{accident}}.
Open this LaTeX fragment in Overleaf.
The following graphic shows the output of this LaTeX code—the document preamble is added automatically by the Overleaf link:
![]()
As you can see, there are three basic commands and they can be nested to get combined effects.
Note: The original text-formatting commands from plain TeX, \it (italicize) and \bf (bold face) will still work in a LaTeX document but their use is discouraged and not recommended because they don't preserve previous styles. For example, when using those old commands you can't apply both italics and bold at the same time.
Italicized text
To make a text italic is straightforward, use the \textit (\emph) command:
Some of the greatest
discoveries in science
were made by \textit{accident}.
Open this LaTeX fragment in Overleaf.
The following graphic shows the output of this LaTeX code—the document preamble is added automatically by the Overleaf link:
![]()
Bold text
To make a text bold use \textbf command:
Some of the \textbf{greatest}
discoveries in science
were made by accident.
Open this LaTeX fragment in Overleaf.
The following graphic shows the output of this LaTeX code—the document preamble is added automatically by the Overleaf link:
![]()
Underlined text
To underline text use the \underline command:
Some of the greatest
discoveries in \underline{science}
were made by accident.
Open this LaTeX fragment in Overleaf.
The following graphic shows the output of this LaTeX code—the document preamble is added automatically by the Overleaf link:
![]()
Emphasising text
Text can be emphasized using the \emph command. Sometimes the \emph command behaves just as \textit, but is not exactly the same:
Some of the greatest \emph{discoveries}
in science
were made by accident.
\textit{Some of the greatest \emph{discoveries}
in science
were made by accident.}
\textbf{Some of the greatest \emph{discoveries}
in science
were made by accident.}
Open this LaTeX fragment in Overleaf.
The following graphic shows the output of this LaTeX code—the document preamble is added automatically by the Overleaf link:
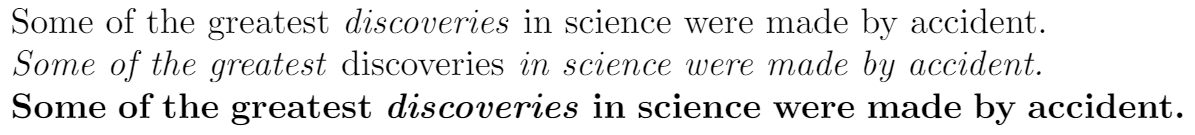
What the \emph command actually does with its argument depends on the context—inside normal text the emphasized text is italicized, but this behaviour is reversed if used inside an italicized text—see example above. Moreover, some packages, e.g. Beamer, change the behaviour of the \emph command.
Full set of examples
The following example collects the various code fragments contained in this article so that you can open them all together in Overleaf.
First example, bold, italics and underline:
Some of the \textbf{greatest} discoveries in \underline{science} were made by \textbf{\emph{accident}}.
\vspace{1.5cm}
Example of italicized text:
Some of the greatest discoveries in science were made by \emph{accident}.
\vspace{1.5cm}
Example of boldface text:
Some of the \textbf{greatest} discoveries in science were made by accident.
\vspace{1.5cm}
Example of underlined text:
Some of the greatest discoveries in \underline{science} were made by accident.
\vspace{1.5cm}
Example of emphasized text in different contexts:
Some of the greatest \emph{discoveries} in science were made by accident.
\textit{Some of the greatest \emph{discoveries} in science were made by accident.}
\textbf{Some of the greatest \emph{discoveries} in science were made by accident.}
Open this LaTeX code in Overleaf.
Further reading
For more information see